-
i) 1d signal with different edge types
-
(a)
(b)
-
(c)
-
-
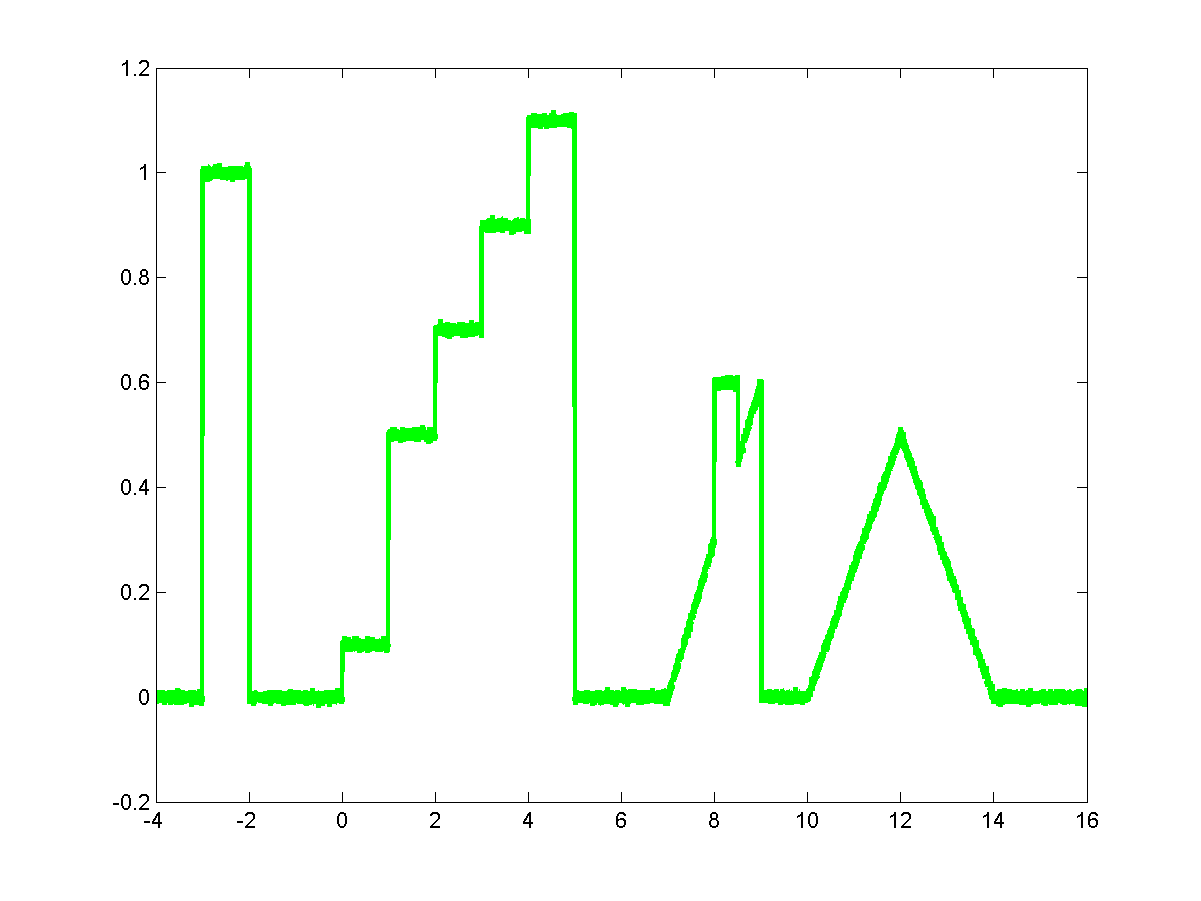
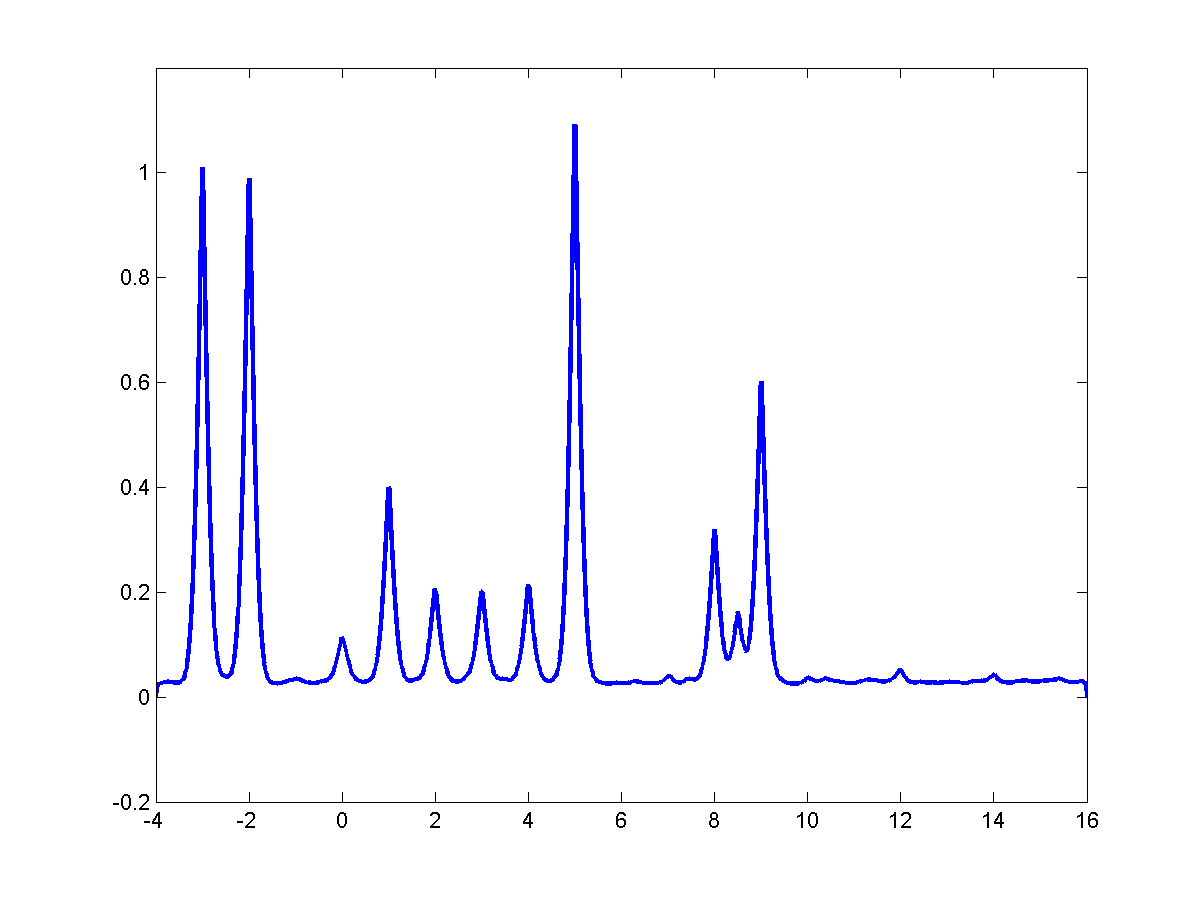
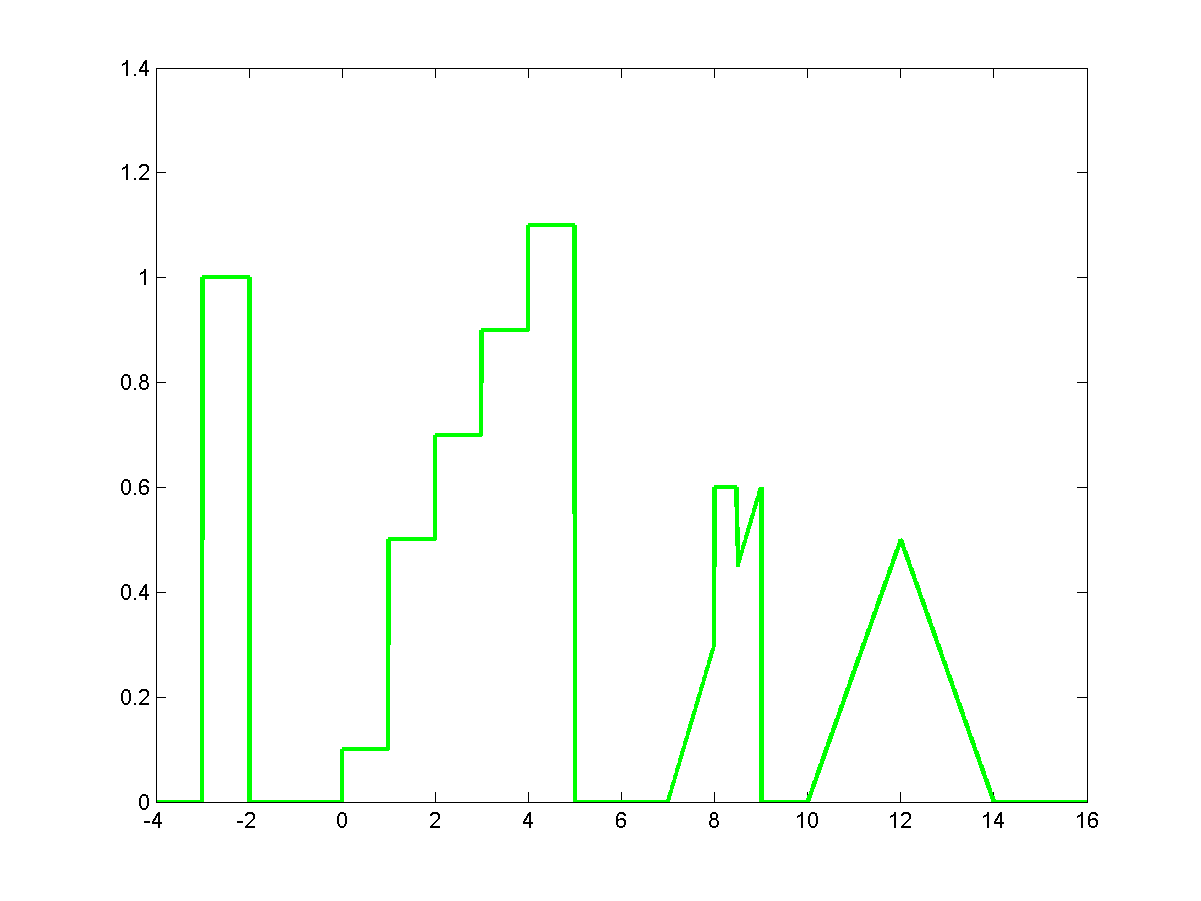
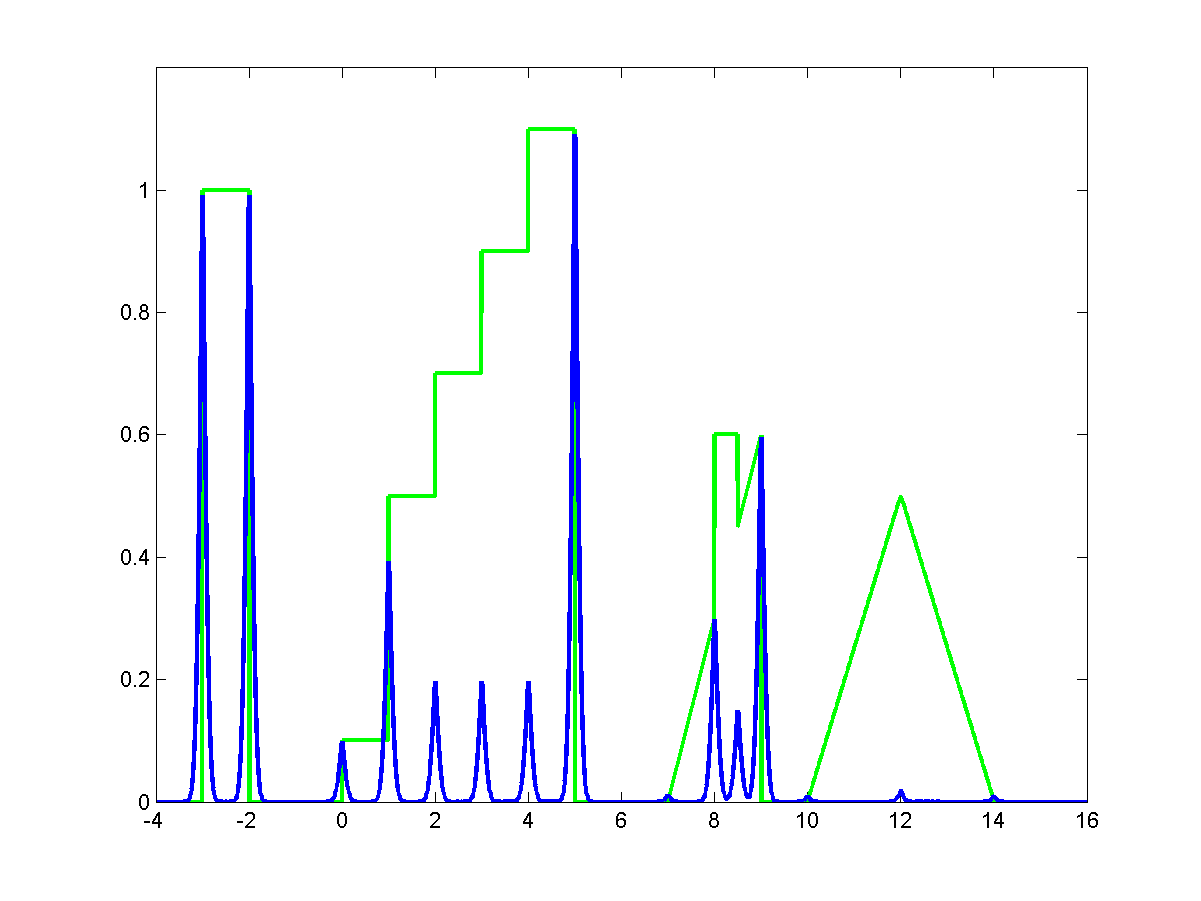
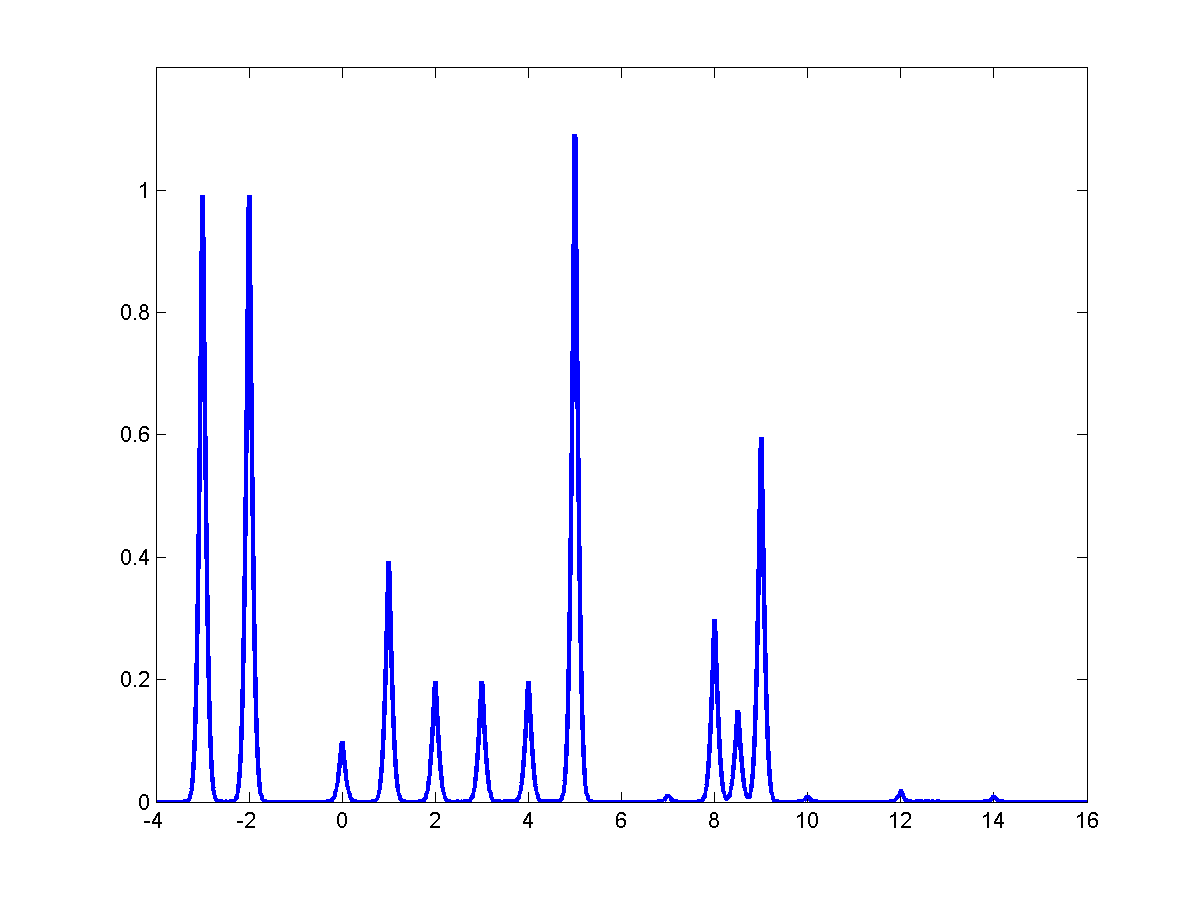
(a) Input signal with various edge types.
-
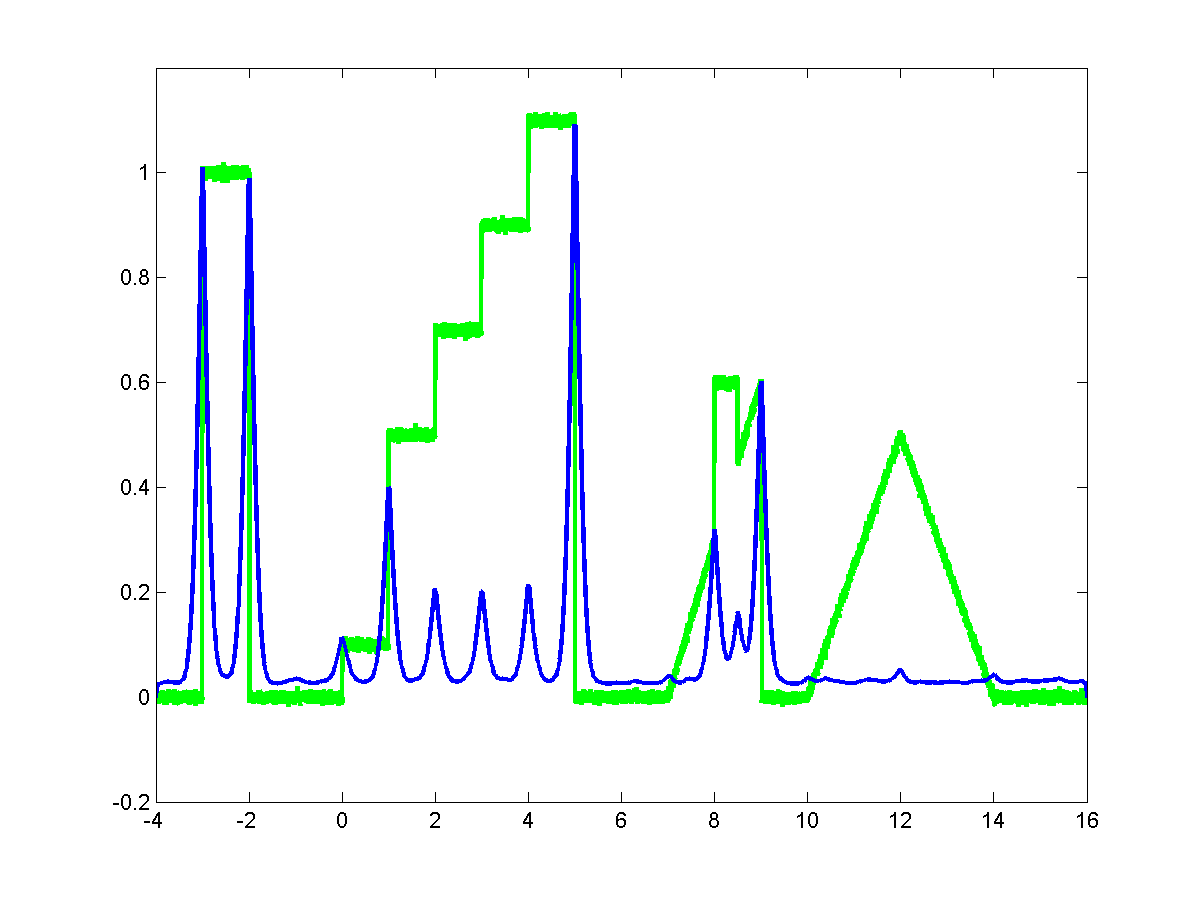
(b) Edge map displayed superimposed to the input signal.
-
(c) Edge map corresponding to l=0.1 and
it =104.
-
iii) SUSAN test image
-

(a)
(b)
-
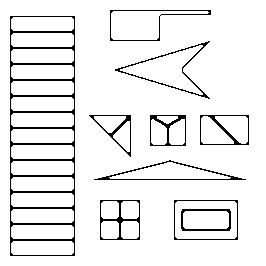
(c)
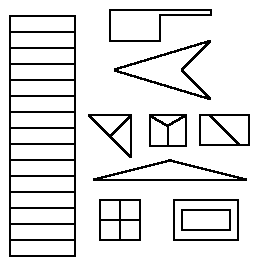
(d)
-
-
(a) SUSAN test image used in the paper 'SUSAN - A new approach to low level image processing' by Smith S.M. and Brady J.M. in International J. Computer Vision 23 (1997) 45-78.
-
(b) Canny edge detection applied to the SUSAN Test image.
-
(c) SUSAN edge detection applied to the SUSAN Test image with parameter t=10.
-
(d) Our edge detector applied to the SUSAN Test image using l=0.1,
it =1 and thres =1.
-
iv) SUSAN test image with an affine perturbation
-

(a)
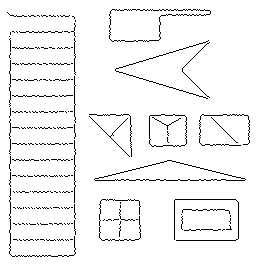
(b)
-

(c)
(d)
-
-
(a) SUSAN test image with the addition of the affine function ƒ(i,j)=5∙(i-j).
-
(b) Canny edges.
-
(c) SUSAN edges with parameter t=10.
-
(d) Our edges for l=0.1,
it =1 and thres =1.
-
v) SUSAN test image with a quadratic perturbation
-

(a)
(b)
-

(c)
(d)
-
-
(a) SUSAN test image with the addition of the quadratic function
ƒ(i,j)=(j-255)2-(i-255)2.
-
(b) Canny edges.
-
(c) SUSAN edges with parameter t=10.
-
(d) Our edges for l=0.1,
it =1 and thres =7.
-
vi) Test image with Gaussian noise
-

(a)

(b)
-

(c)

(d)
-
-
(a) Test image with the addition of Gaussian noise.
-
(b) Canny edges with s=3.
-
(c) The edges displayed in this picture have been obtained by applying
twice the SUSAN algorithm.
When applied the first time, the SUSAN algorithm filters the Gaussian noise and returns a binary image
with sligthly perturbed edges. By applying again the SUSAN algorithm on the filtered image, one is then able to extract the edges of the
background picture.
-
(d) Our edges for l=0.001,
it =1 and thres =90.
-
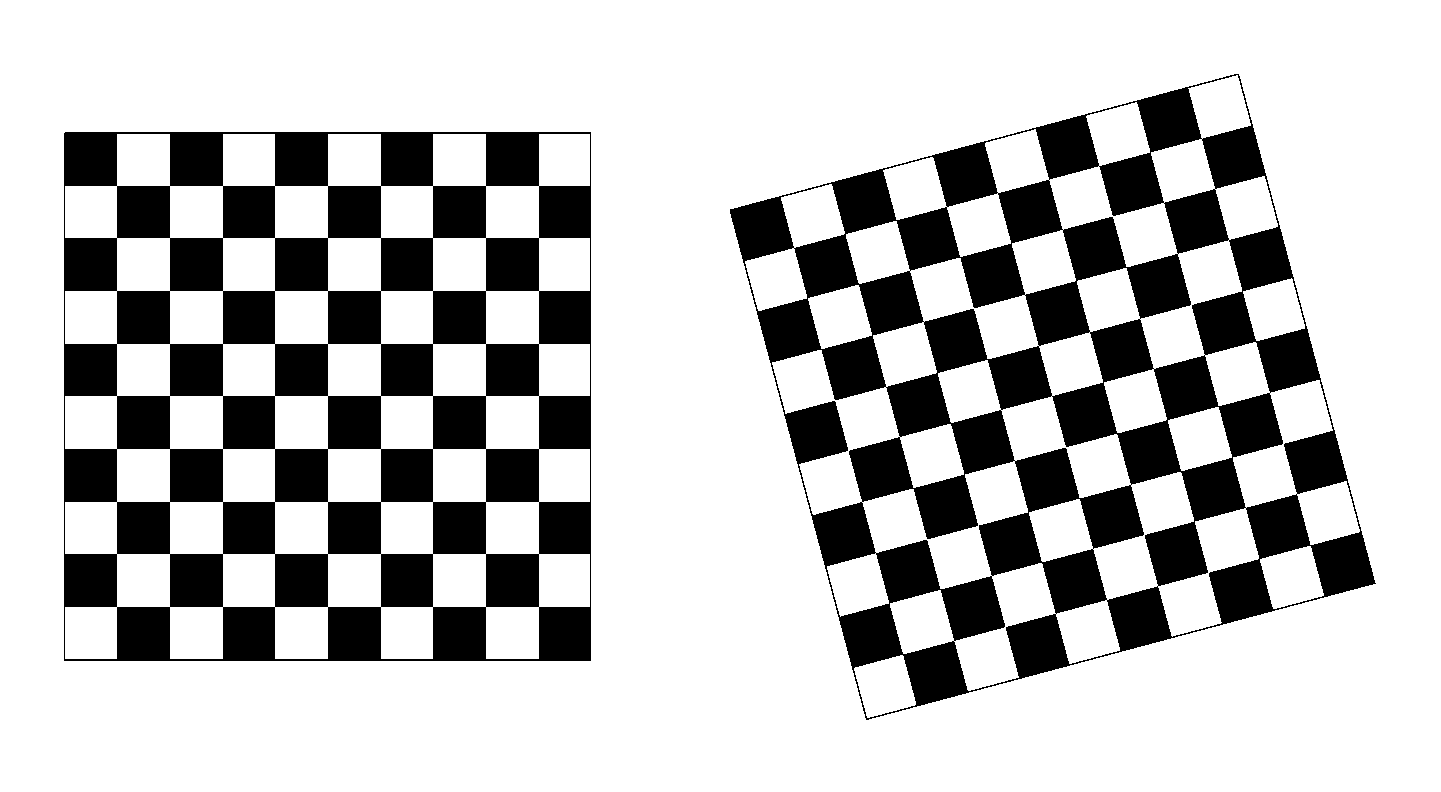
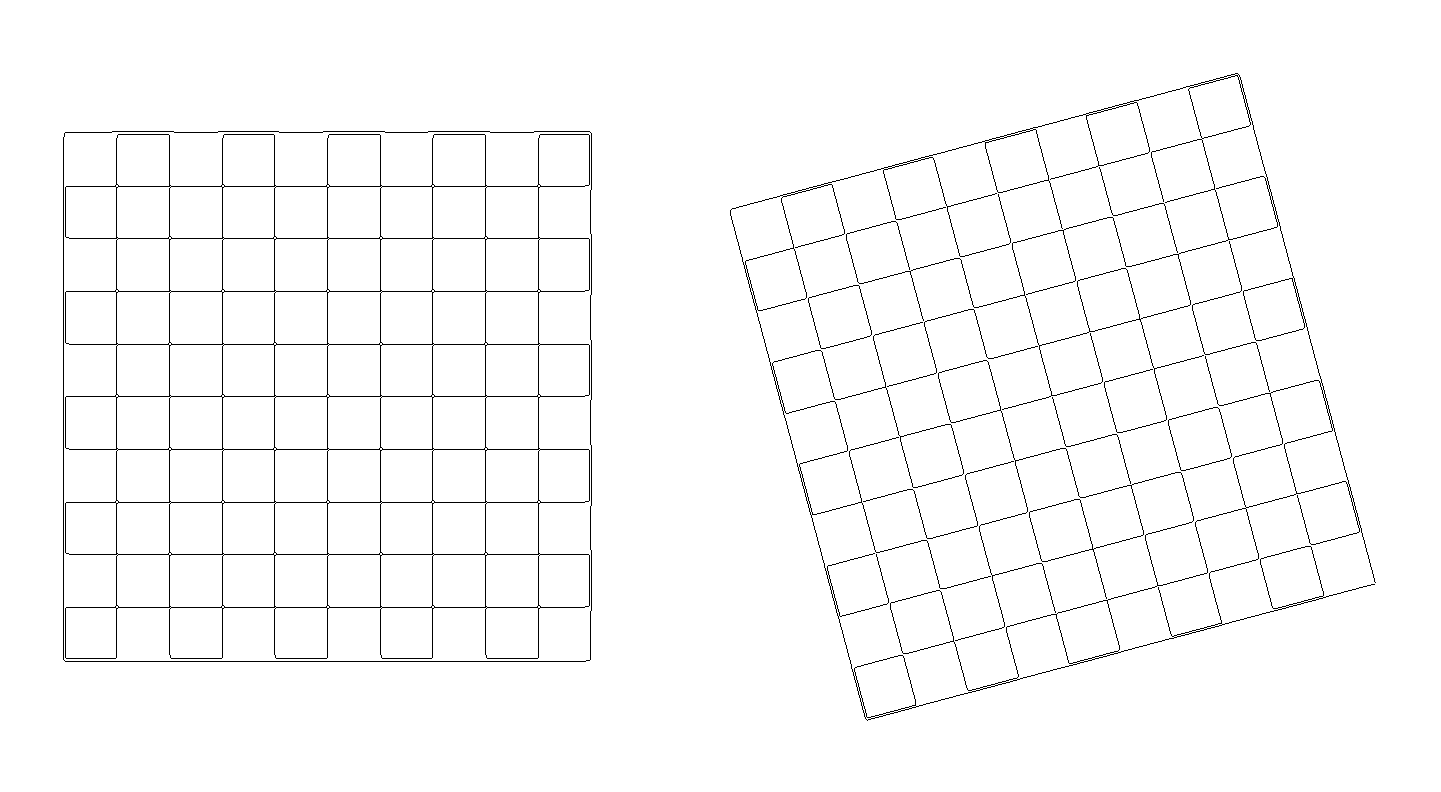
vii) Chessboard test image
-
(a)
(b)
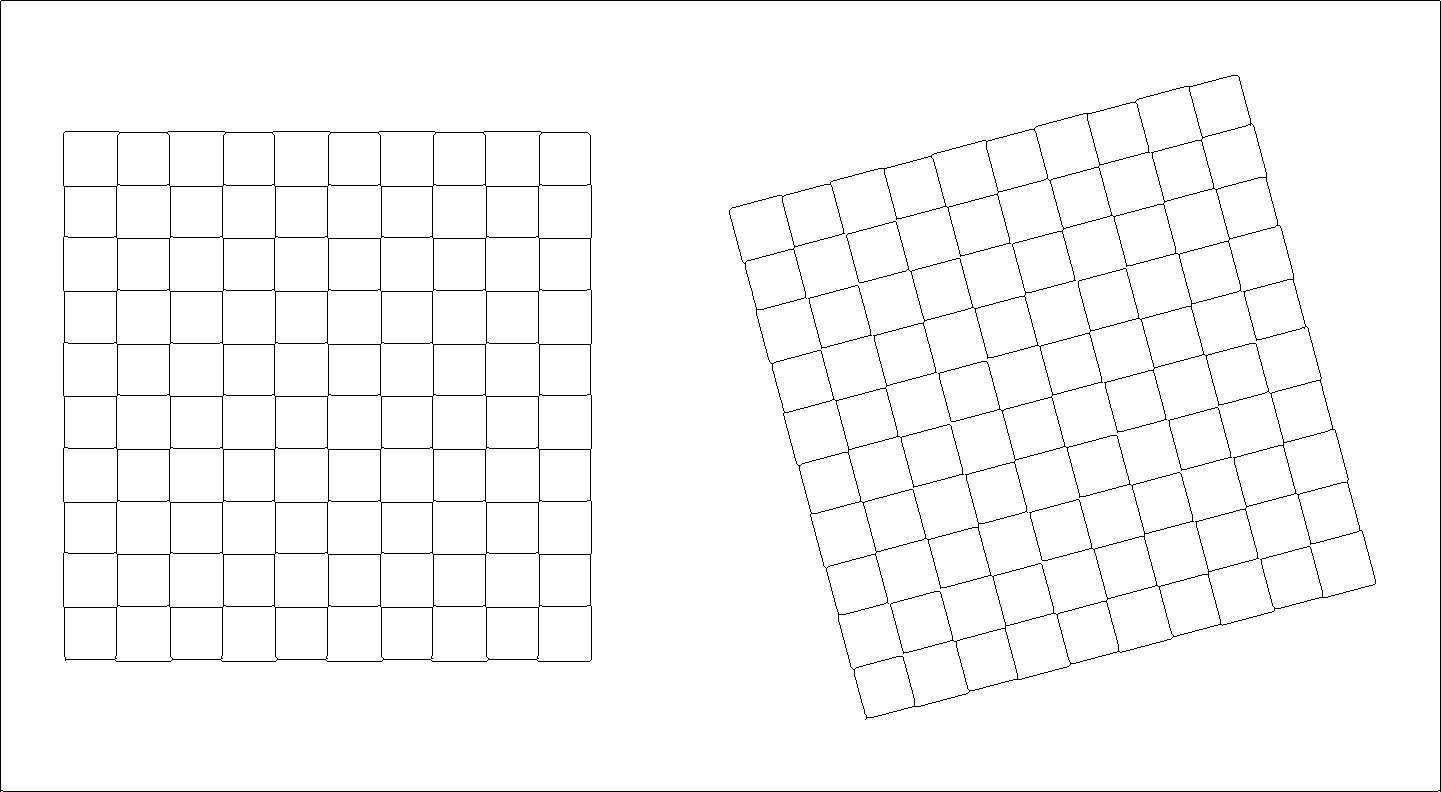
(c)
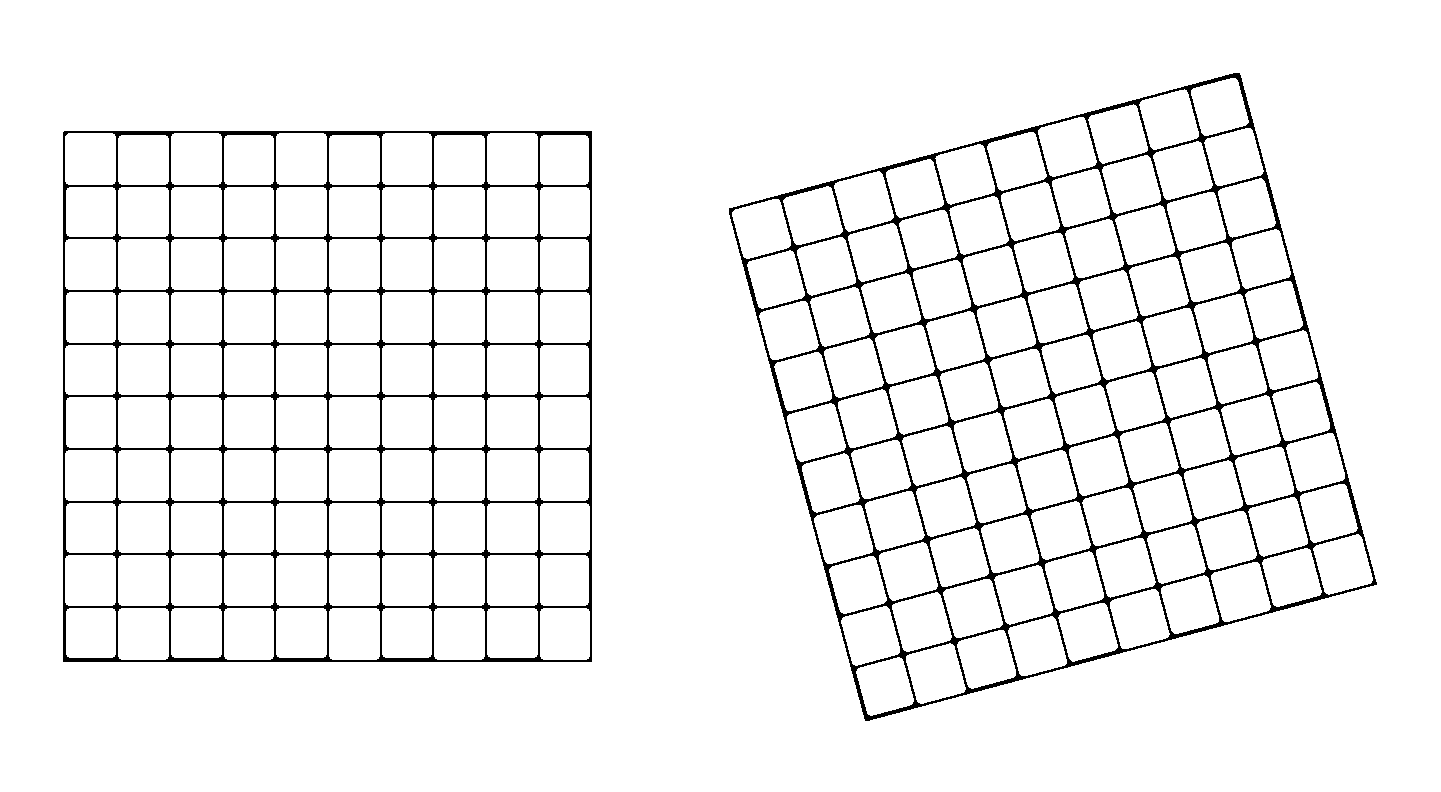
(d)
-
-
(a) Chessboard test image.
-
(b) Canny edges.
-
(c) SUSAN edge detector.
-
(d) Our edges for l=0.1,
it =10 and thres =190.